SPOT 6-7
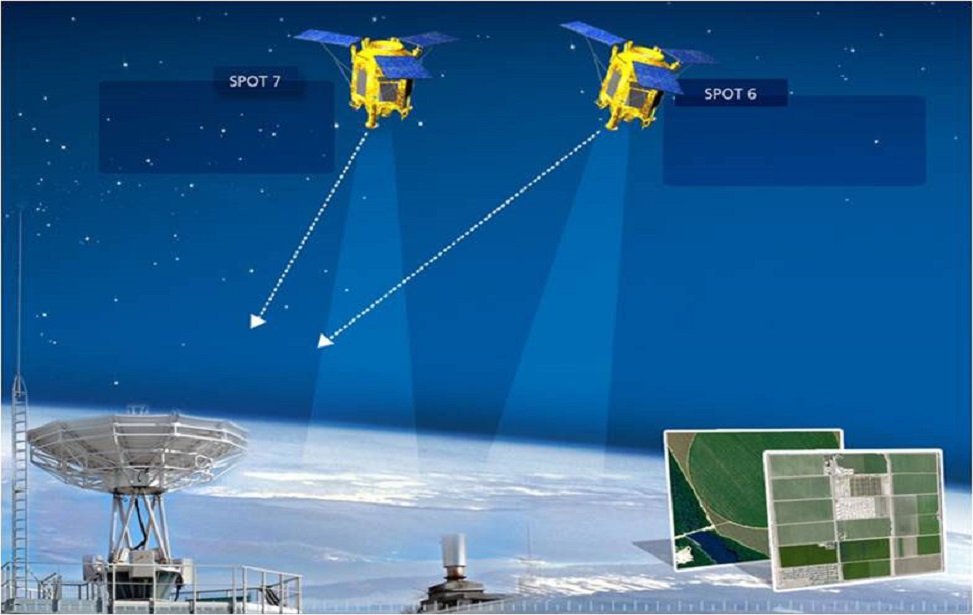
SPOT-6 and SPOT-7, the first twins of the Spot family, are positioned 180 ° from each other on the orbit. Recurring purchases on a daily basis for any point in this feature.
SPOT-6 and SPOT-7 provide a 1.5m high image with five spectral bands visible, simultaneously detected and positionally overlapping. Standard products can be provided in the natural color category as orthorectic.
AOI Filiz obtains convenience in obtaining data of the desired region with its features given in order and North-South direction.
With its upgraded and coded services, the transmission of information is provided at a high level.
SPOT 5
SPOT-5, the fifth satellite of the Spot series, was launched on May 4, 2002. There are two HRG sensors derived from the HRVIR devices on the SPOT-4 satellite, capable of high resolution detection on the satellite. These sensors can provide data with a resolution of 2.5 meters to 5 meters in panchromatic detection mode and 10 meters of resolution or better in multispectral detection mode.
There is an HRS sensor on the satellite that can detect in panchromatic mode. With HRS, stereo image pairs that can define surface relief can be obtained through forward and backward views. Digital Elevation Models are created from stereo image pairs that provide the height information of the earth.
PLÉİADES
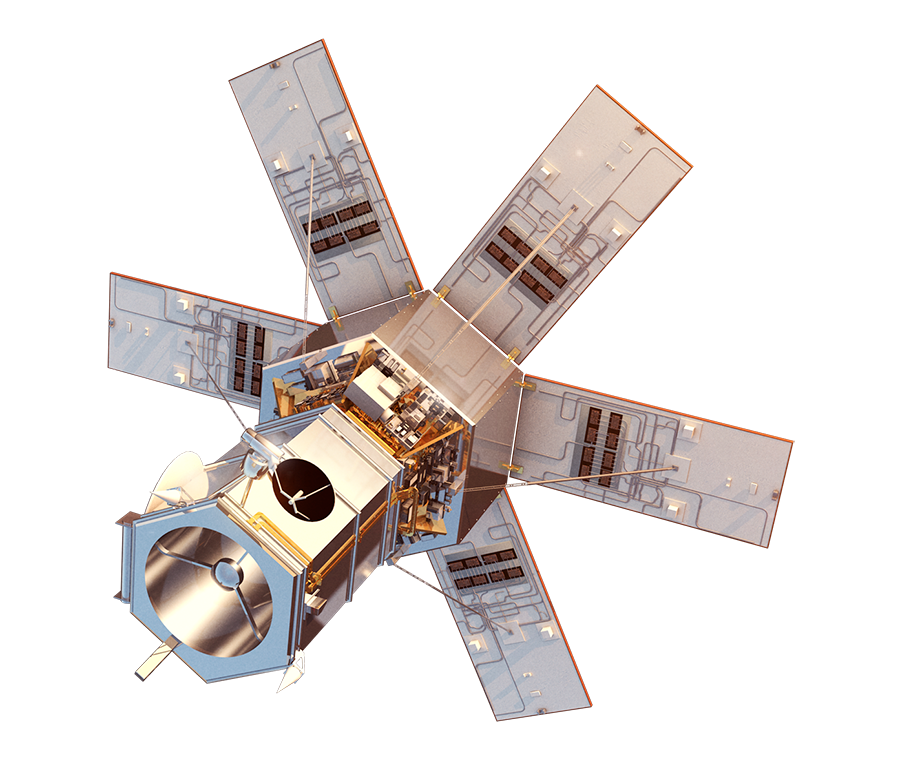
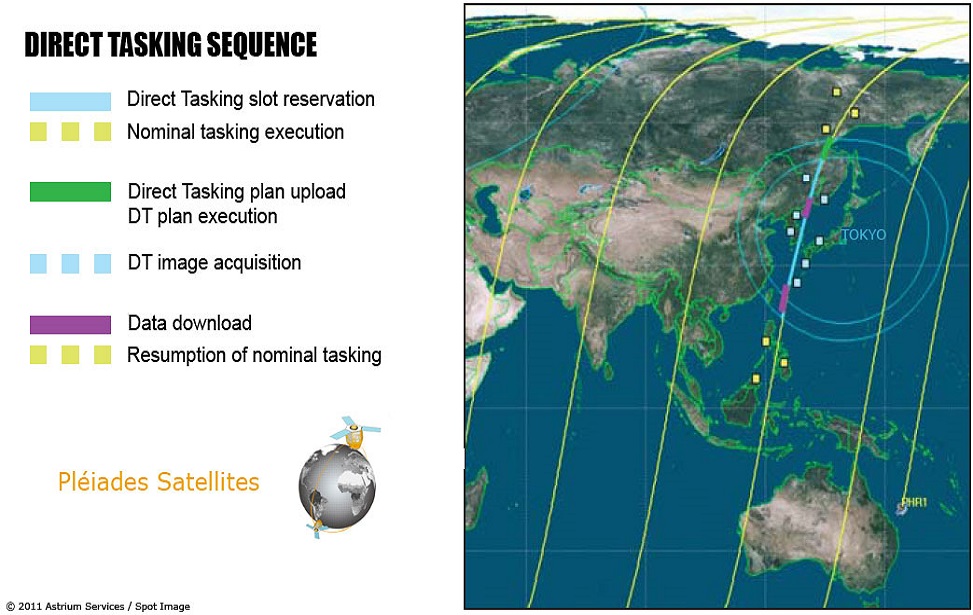
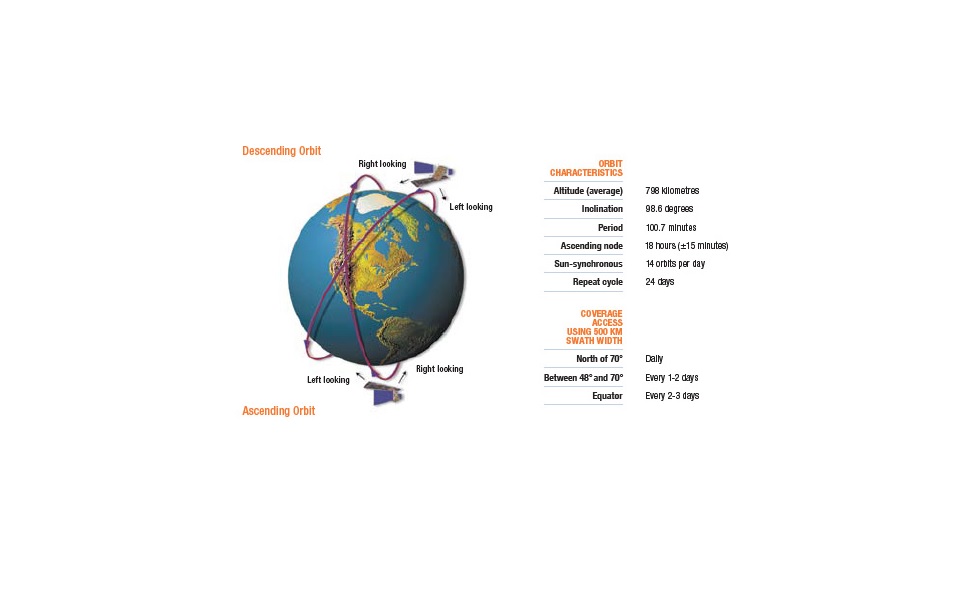
Pléiades 1A and Pléiades 1B operate on the same sun-synchronous circular orbit 180 ° apart. These twin satellites, which produce very high spatial resolution optical data, have the capacity to visit a point on earth twice a day. Due to these advantages, they can be used for both civilian and military observation purposes such as engineering and construction project areas, mines, military complexes, conflict areas, crisis and disaster areas, natural risk areas, evacuation and rescue operations.
The Pléiades 1A was launched on November 16, 2011, and The Pléiades 1B on December 2, 2012. The distribution of the images of the satellites produced by the Astrium company is done by Spot Image.
RadarSAT 1-2
Radarsat-1, Canada’s first commercial surveillance satellite, was placed in orbit on 4 November 1995 and continued to provide images until 29 March 2013. The satellite, whose orbit height is 798km from the ground, uses Artificial Aperture Radar sensors in the C band at 5.3 GHz microwave frequency. Depending on the angle of incidence of the beams to the earth, images with different resolution and coverage area can be obtained. While it can provide an image in an area of 50km to 50km with the highest resolution of 8m, it can give an image in an area of 500km to 500km with 100m resolution.
Radarsat-2 was put into orbit on December 14, 2007 as a joint effort of MDA and the Canadian Space Agency. The term of office is designed as a minimum of 7 years. Unlike RSAT-1 satellite, Ultra Fine Beam mode with 3m spatial resolution has been added, 3mx1m resolution spotlight feature with 18km swath width has been added. The polarization, which is unique in RSAT-1, has been increased to four as HH HV VV and VH, and its capacity has been increased so that the direction of view can be both right and left.
METEOSAT
The second generation Meteosat Program (MSG) covers a series of satellites in geosynchronous orbit. This satellite system program, located in orbit 36000km from the equator, is run by EUMETSAT. In addition to providing numerical weather forecast data, it is used to detect instant weather changes, atmospheric images, and predict effective weather events such as storm fog for up to 6 hours.
WorldView-1
- WorldView-1 was released in September 2007.
- It has a band width of 17.7 km in rare.
- It has a panchromatic band of 400-900 nm.
- It has 50 cm GSD in rare and 55 cm GSD in 20 ° off-rare.
- Dynamic range is 11 bits.
- It has a temporal resolution of 1.7 days for 1 meter or less GSD, and a
- temporal resolution of 5.4 days for an off-rare angle less than 20 ° (0.55 m GSD).
- It has CE90 accuracy of <4.0 m without ground control.
- One-pass stereoscopic image acquisition ensures image continuity and quality consistency.
- It has a daily dredging capacity of 1.3 million km².
WorldView-2
- WorldView-2, released in October 2009, is the first high resolution 8-band multiband commercial satellite.
- It has a band width of 16.4 km in rare.
- A panchromatic (450 – 800 nm),
- It has eight multispectral bands (Coastal: 400 – 450 nm, Blue: 450 – 510 nm, Green: 510 – 580 nm, Yellow: 585 – 625 nm, Red: 630 -690 nm, Red Edge: 705 – 745 nm, Near- IR1: 770 – 895 nm, Near-IR2: 860 – 1040 nm).
- With panchromatic band, it rarely has 0.46 m GSD, 20 ° off-rarely 0.52 m GSD.
- With the multispectral band, it rarely has 1.85 m GSD and 20 ° off-rarely 2.07 m GSD.
- Dynamic range is 11 bits.
- It has a temporal resolution of 1.1 days for 1 meter or less GSD, and a temporal resolution of 3.7 days for an off-rare angle less than 20 ° (0.52 m GSD).
- It has CE90 accuracy of <3.5 m without ground control.
- One-pass stereoscopic image acquisition ensures image continuity and quality consistency.
- With its 8-band multispectral capacity, it enables precise change analysis.
- It has a daily scanning capacity of 1 million km².
GeoEye-1
The GeoEye-1 satellite was launched on September 6, 2008 from Vandenberg Air Base, California.
At the time of its introduction, GeoEye-1 was the highest resolution satellite on the market.
In Nadir, it has a band width of 15.3 km at an altitude of 681 km and a width of 17.3 km at an altitude of 770 km.
Spectral bands it has:
Panchromatic: 450 – 800 nm
4 MultispectralRed: 655 – 690 nm Green: 510 – 580 nm
Blue: 450 – 510 nm Near-IR: 780 – 920 nm
At an altitude of 681 km, rarely; It has 0.41 m GSD with panchromatic band, 1.65 m GSD with multispectral band.
At an altitude of 770 km, rarely; It has 0.46 m GSD with panchromatic band, 1.84 m GSD with multispectral band.
Dynamic range is 11 bits.
It has a temporal resolution of 2.3 days for a detection angle of 30 ° at an altitude of 681 km, 2.6 days for a detection angle of 30 ° and less at an altitude of 770 km.
It has 5 m CE90 accuracy.
One-pass stereoscopic image acquisition ensures image continuity and quality consistency.
It has a daily scanning capacity of 700,000 km².
WorldView-3
- It is the Maxar satellite, launched on August 13, 2014, licensed by NOAA to receive eight-band shortwave infrared (SWIR) images.
- It has a band width of 13.1 km in rare.
- It rarely has 0.31 m GSD with panchromatic band, and 0.34 m GSD at 20 ° off-rarely.
- With the multispectral band, it rarely has 1.24 m GSD and 20 ° off-rarely 1.38 m GSD.
- It rarely has 3.70 m GSD with SWIR band and 4.10 m GSD at 20 ° off-rare.
- It rarely has 30m GSD with CAVIS tape.
- Dynamic range is 11 bits for panchromatic and mulsipectral bands and 14 bits for SWIR band.
- It has a temporal resolution of less than 1 day for 1 meter of GSD, and a temporal resolution of 5.4 days for an off-rare angle less than 20 °.
- It has CE90 accuracy of <3.5 m without ground control.
- It eliminates the problem of time-dependent changes in scanned areas with mono and stereo image acquisition capability and temporal resolution of less than 1 day.
- It enables precise position determination without ground control points.
- It has a daily scanning capacity of 680.000 km².
WorldView-4 (Not in use)
The WorldView-4 satellite was launched from Vandenberg Air Base, California, on November 11, 2016 (PST).
WorldView-4 has been the highest resolution satellite on the market since its introduction.
It has a band width of 13.2 km in the rare.
Spectral bands it has:
Panchromatic: 450 – 800 nm
4 MultispectralRed: 655 – 690 nm Green: 510 – 580 nm
Blue: 450 – 510 nm Near-IR: 780 – 920 nm
With panchromatic band, it rarely has 0.31 m GSD, 20 ° off-rare 0.34 m GSD, 56 ° off-rare and 1 m GSD.
With the multispectral band, it rarely has 1.24 m GSD, 20 ° off-rare 1.38 m GSD, 56 ° off-rare has 4 m GSD.
Dynamic range is 11 bits.
It has a temporal resolution of less than 1 day for 1 meter of GSD.
It has CE90 accuracy of <5 m without ground control.
With its large mono and stereo image collection capacity and high temporal resolution, it eliminates the problem of time-dependent changes in the scanned areas.
It has a daily scanning capacity of 680.000 km².
It enables precise position determination without ground control points.
Maxar; On January 7, 2019, it announced that the WorldView-4 satellite could not be used due to a gyroscope malfunction.
 CSCRS İTÜ – Center for Satellite Communications and Remote Sensing
CSCRS İTÜ – Center for Satellite Communications and Remote Sensing