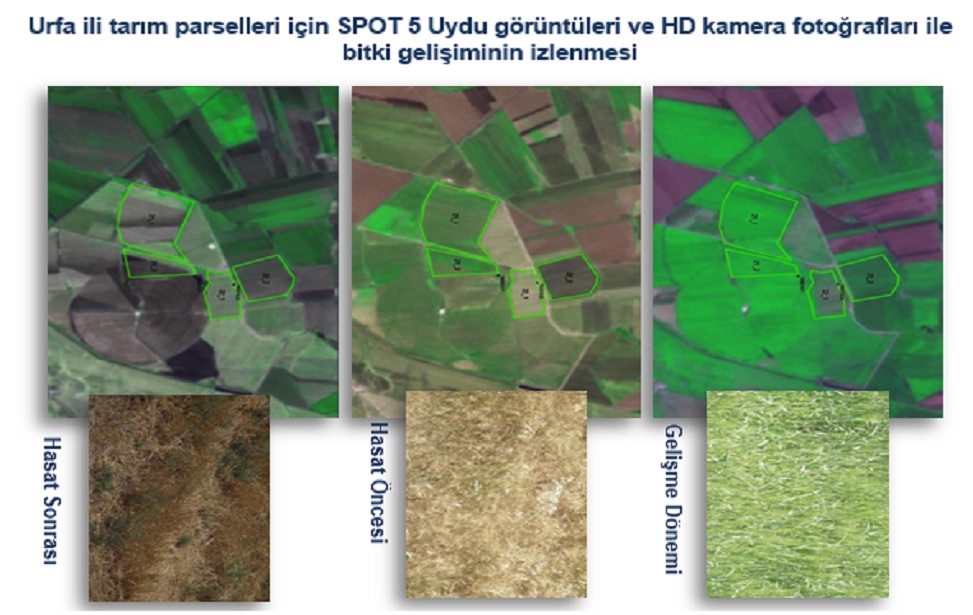
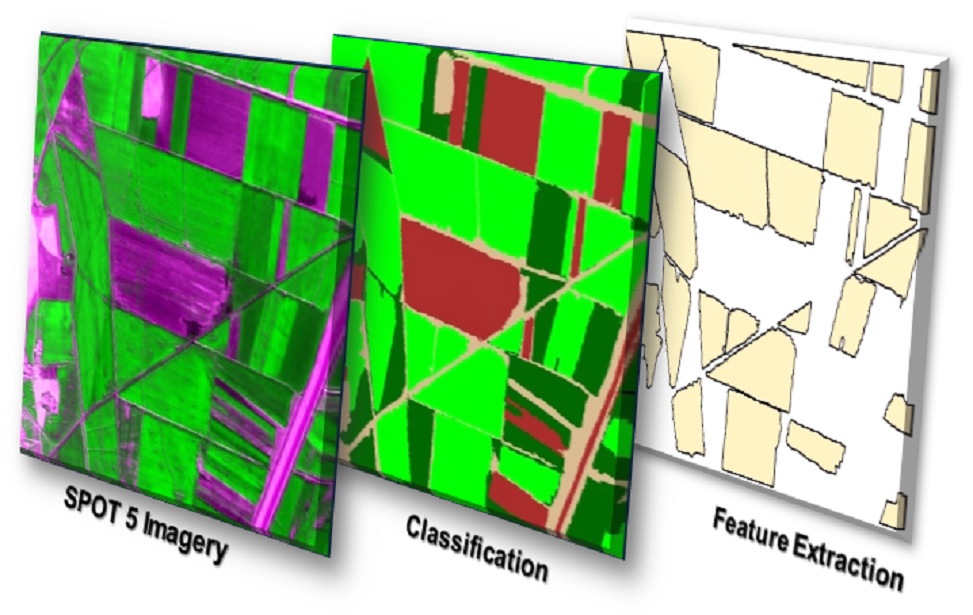

Agricultural Monitoring and Information System (AMIS)
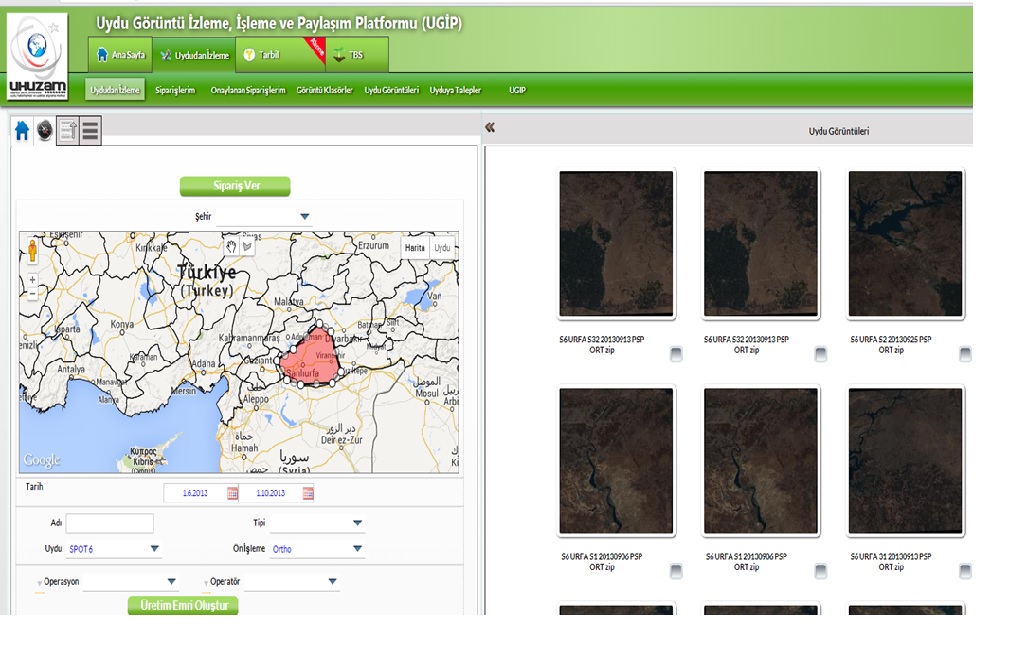
ITU CSCRS Within the scope of the Agricultural Monitoring and Information System (AMIS) project, periodic monitoring of cultivated areas with high spatial resolution satellite images during the phenological period, determination of product types and spatial distribution by object-based image classification, production of plant indexes for tracking product development, produced image, classification and the transfer of plant index data and statistical results reports to the relevant units affiliated to the Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Livestock. With 600 TB online data storage server and fast fiber network infrastructure, CSCRS shares the data with the help of UGIP and PARIS modules that work in integration with the AMIS web interface. With UGIP, which is a satellite image sharing platform, the end user can scan archives in the relevant geographic area, in the specified date range, with the selected satellite type and image processing level information, and download the images they have determined through the web interface with multiple selection among the results. Thanks to the PARIS platform, the end user can see the current satellite images, plant index data, crop planting pattern information in layers on the agricultural parcel / parcels he / she is interested in or owns via mobile devices or standard computers. In addition, authorized GTHYB personnel can perform local data entry, association and verification with satellite image-based data on parcel basis and update the database during field studies.
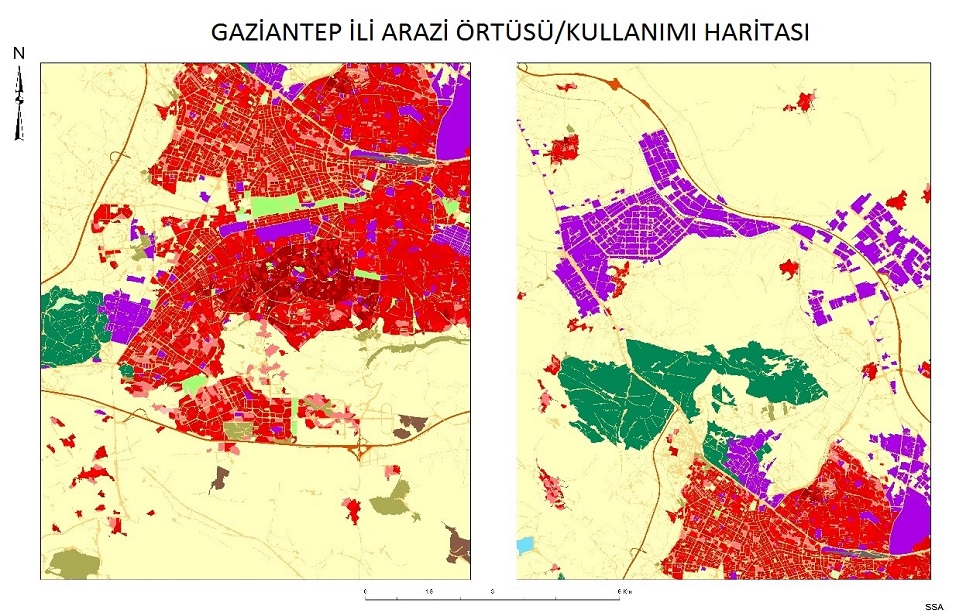
Creating a National Land Cover Database
Developing an international land cover / use classification system using high spatial resolution satellite images and proposing an appropriate methodology in this context.
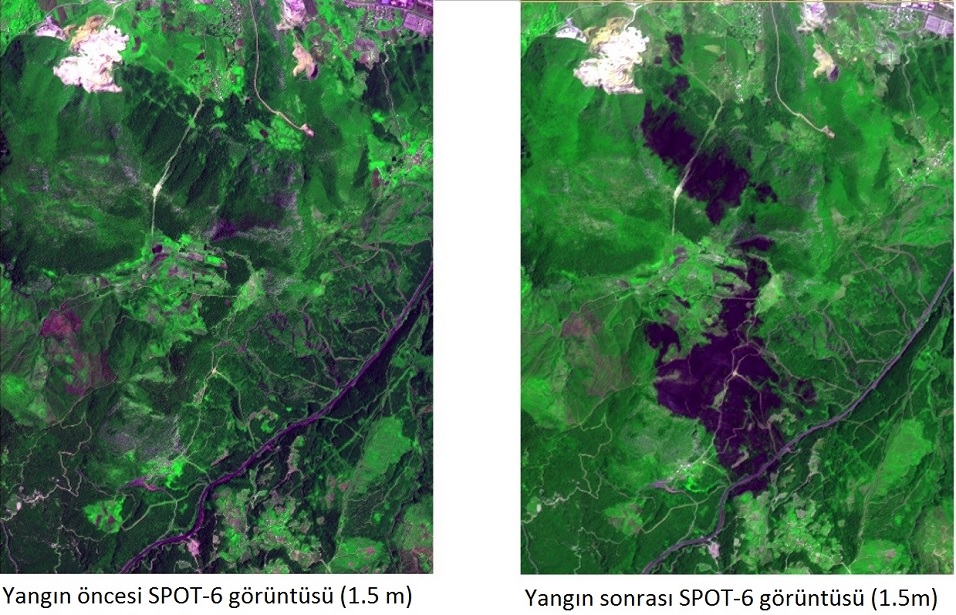
Damage Analysis After Forest Fire with Spot 6 Images
Detecting areas affected by fire with near real-time Spot 6 image acquisition and object-based classification after fire and comparing with stand map to identify damaged species.
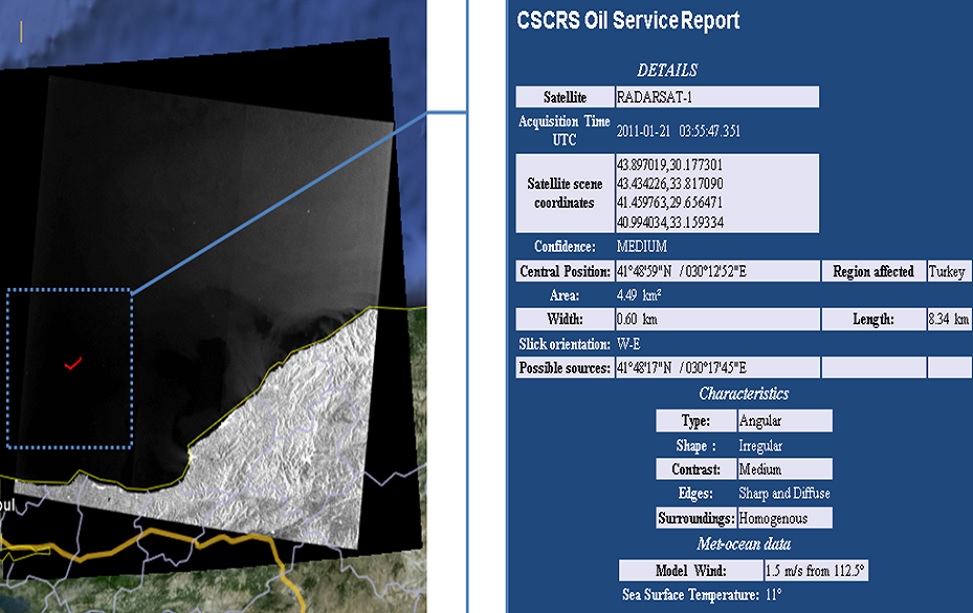
Shipborne Pollution Detection with Radar Images
Direct download of near real-time images to the center and fast analysis (30 minutes) capability to detect ship-originated pollution in open seas and report them to relevant units.
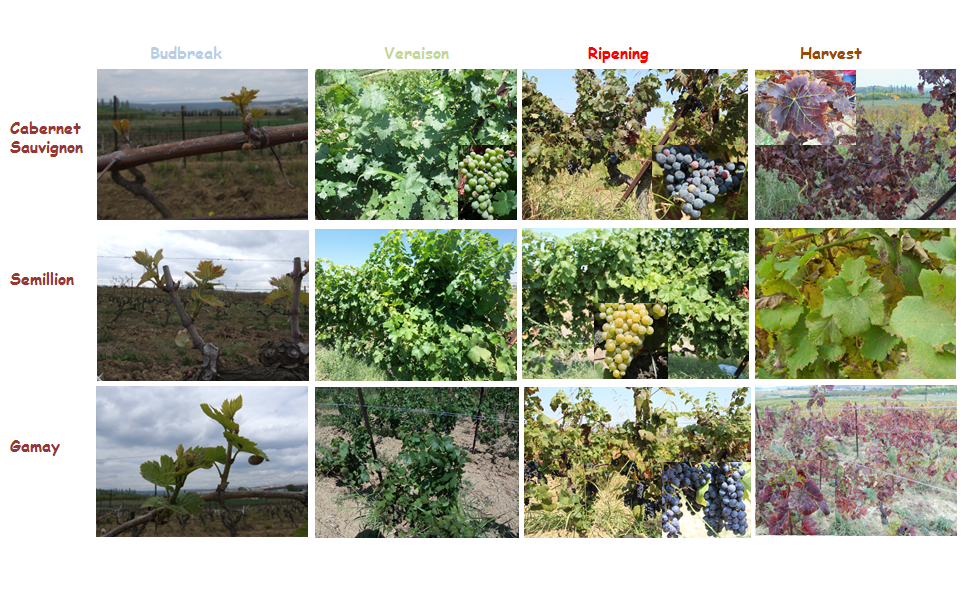

Remote Sensing and Detection of Bond Areas with GIS
Determination of the spatial distribution of vineyard areas, creation of grape spectral libraries and determination of grape varieties from high resolution satellite images with the help of this library and determination of suitable areas for viticulture in Tekirdağ province with satellite images and terrestrial measurements.
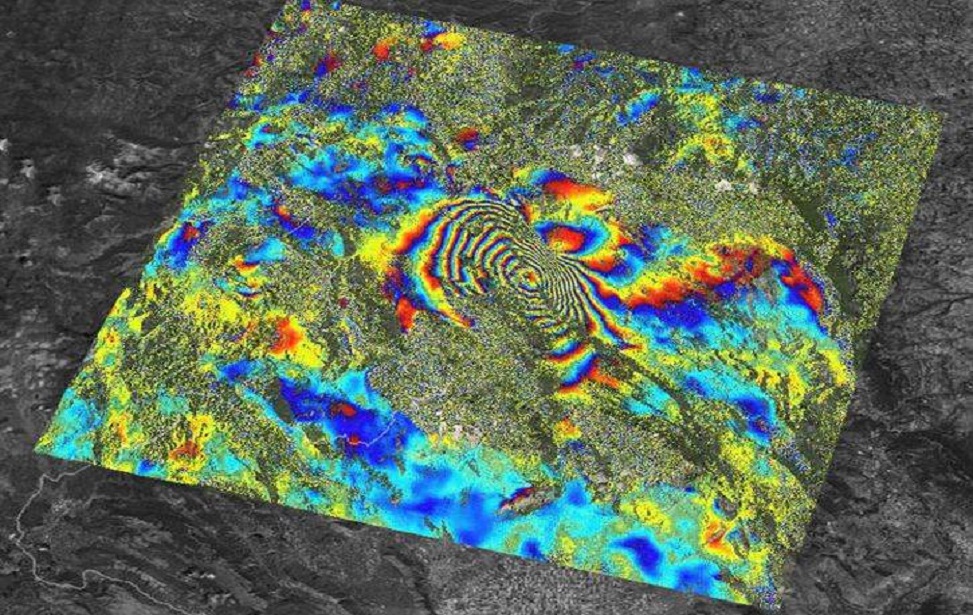
Italy – INSAR Project
Radarsat 1 images used in determining the deformation occurring in mining areas in Italy were provided by CSCRS.
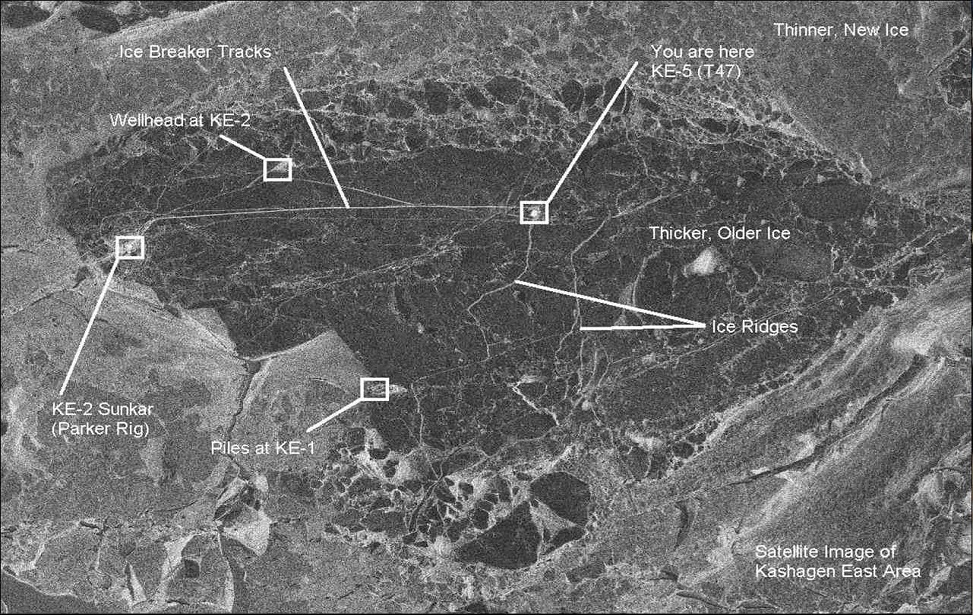
Caspian sea ice monitoring
Ice movement monitoring among the oil rigs at Caspian sea Italy InSAR project: Change detection using interferometre (Earthquake)

Digital Terrain Model Generation with Spot 6 Tri-Stereo Images
Digital Terrain Model generation using tri-stereo satellite images obtained from Spot 6 and Pleiades satellites.
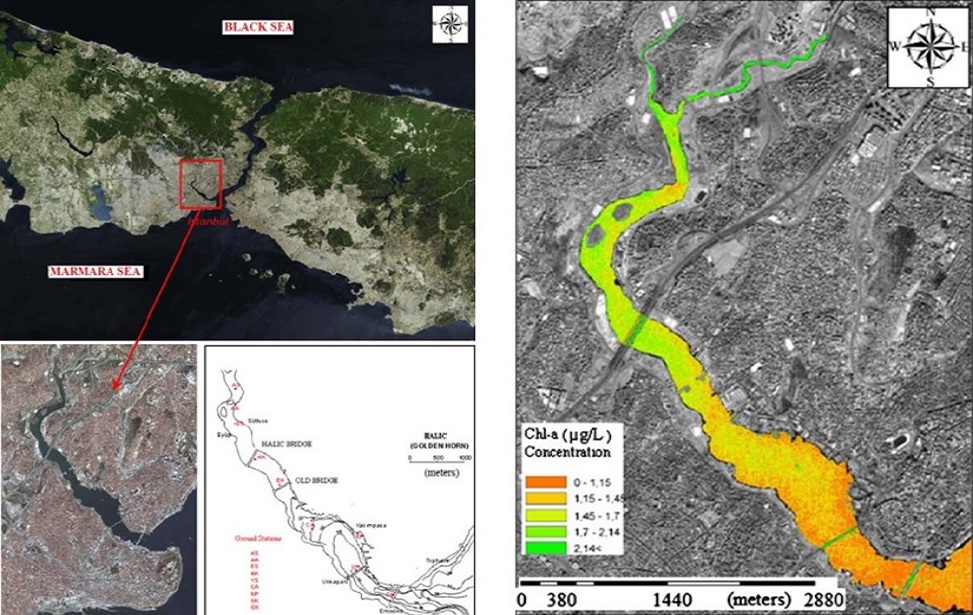
Water Quality Analysis with Satellite Images – Haliç Example
Determination of water quality and spatial distribution of pollutants in the Haliç by using satellite images and simultaneous ground measurements.
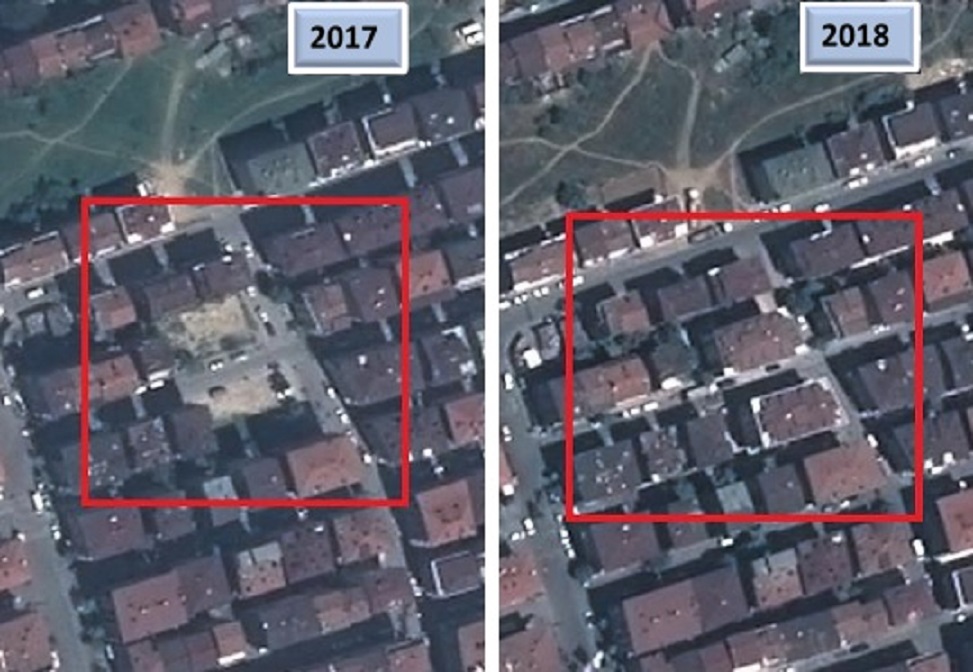

Zoning Peace – Building Change Detection
The application of determination of building changes is carried out with Pleiades 1A and 1B satellites.
 CSCRS İTÜ – Center for Satellite Communications and Remote Sensing
CSCRS İTÜ – Center for Satellite Communications and Remote Sensing